Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- 잔
- 컴퓨터공학 #Java #자바 #클래스 #객체 #인스턴스
- 컴퓨터공학 #자료구조 #스택 #c++ #알고리즘 #백준문제풀이
- HTML #CSS
- 컴퓨터공학 #c #c언어 #문자열입력
- BOJ #컴퓨터공학 #C++ #알고리즘 #자료구조
Archives
- Today
- Total
영벨롭 개발 일지
[C++]유용한 STL 알고리즘 함수 본문
[ 유용한 STL 알고리즘 함수 ]
| STL 함수 | 설명 |
| std::binary_search() | 이진 검색을 이용하여 컨테이너에서 원소 하나를 찾습니다. 해당 원소가 있으면 true / 없으면 false (조건: 컨테이너가 정렬되어 있어야함) |
| std::search() | 컨테이너에서 일련의 원소들을 찾고 그 시작 반복자를 반환합니다. |
| std::upper_bound() | 컨테이너에서 주어진 값보다 큰 원소가 나타나기 시작하는 위치의 반복자를 반환합니다. (조건: 컨테이너가 정렬되어 있어야함) |
| std::lower_bound() | 컨테이너에서 주어진 값보다 작은 원소가 나타나기 시작하는 위치의 반복자를 반환합니다. (조건: 컨테이너가 정렬되어 있어야함) |
| std::partition() | 분할 연산을 수행하고, 주어진 피봇보다 작은 원소는 피봇 왼쪽으로 옮기고 피봇 보다 큰 원소는 피봇 오른쪽으로 옮깁니다. |
| std::partition_copy() | 분할 연산을 수행하고, 그 결과를 별도의 두 배열로 반환합니다. |
| std::is_partitioned() | 주어진 피벗을 기준으로 분할이 되어 있는지를 검사합니다 |
| std::stable_partition() | 분할 연산을 수행하며, 각 파티션 원소는 원본 순서를 유지합니다. |
| std::sort() | 컨테이너 원소를 정렬합니다. |
| std::stable_sort() | 컨테이너 원소를 정렬하되, 서로 순위가 같은 원소에 대해 원본 순서가 변경되지 않도록 정렬합니다. |
| std::partial_sort() | 컨테이너 전체가 아니라 일부 구간에 대해서 정렬합니다. |
| std::merge() | 두 개의 입력 컨테이너를 합칩니다. 이때 두 컨테이너의 원소 순서는 그대로 유지됩니다. |
| std::nth_element() | 컨테이너에서 n번째로 작은 원소를 반환합니다. |
| std::accumulate() | 컨테이너 원소의 누적 합을 계산합니다. 이 함수는 다른 외부 함수를 지정하여 누적 합이 아닌 다른 연산을 수행할 수도 있습니다. |
| std::transform() | 컨테이너와 함수가 주어지면, 컨테이너의 모든 원소에 대해 해당 함수를 적용하여 값을 수정합니다. |
| std::reduce() | 지정한 범위의 원소에 대해 리듀스 연산을 수행하고 결과를 반환합니다. |
[ 예제 ]
- 검색: binary_search & search()
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
vector<int> arr = { 10, 9, 7, 2, -1, 0, 10, 10, 1, 3 };
//binary_search는 sort 필수 !
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
bool ret = binary_search(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 10);
cout << "binary_search: " << ret << endl;
vector<int> a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
vector<int> b = { 1, 2, 3 };
auto it = search(a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin(), b.end());
if (it != a.end()) {
cout << "vector b는 " << (it - a.begin()) << "번째 인덱스에 위치" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "vector a안에 vector b가 없음" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- 이진검색 기반 상한/하한: upper_bound(), lower_bound()
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
vector<int> arr = { 10, 9, 7, 2, -1, 0, 10, 10, 1, 3 };
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
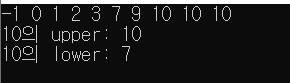
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
auto upper = upper_bound(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 10);
auto lower = lower_bound(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 10);
cout << "10의 upper: " << upper - arr.begin() << endl;
cout << "10의 lower: " << lower - arr.begin() << endl;
return 0;
}
- partitioning
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
// is_partitioned & partition
vector<int> arr = { 2, 1, 5, 6, 8, 7 , 3 };
// 4보다 작은 원소는 왼쪽에 크거나 같은 원소는 오른쪽에
partition(arr.begin(), arr.end(),
[](int x) { return x < 4; });
// partitioning 되었는지 확인
bool ret = is_partitioned(arr.begin(), arr.end(),
[](int x) { return x < 4; });
if (ret) {
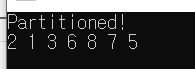
cout << "Partitioned!" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Not partitioned" << endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
반응형
'Programming Language > C & C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++]이분 탐색 lower_bound & upper_bound 사용하기 (0) | 2022.05.06 |
|---|---|
| [C++]STL 해시 테이블 unordered_set과 unordered_map (0) | 2022.04.26 |
| [C++]순열 next_permutation STL 사용하기 (0) | 2022.03.31 |
| [C++]std::array 클래스 사용법 (0) | 2022.03.29 |
| [C++]system() 함수 - 몇 가지 명령어 사용해보기 (0) | 2022.03.06 |




