| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- BOJ #컴퓨터공학 #C++ #알고리즘 #자료구조
- HTML #CSS
- 컴퓨터공학 #Java #자바 #클래스 #객체 #인스턴스
- 컴퓨터공학 #자료구조 #스택 #c++ #알고리즘 #백준문제풀이
- 컴퓨터공학 #c #c언어 #문자열입력
- 잔
- Today
- Total
영벨롭 개발 일지
[백준 BOJ][C++]2250번 트리의 높이와 너비 풀이: DFS 본문
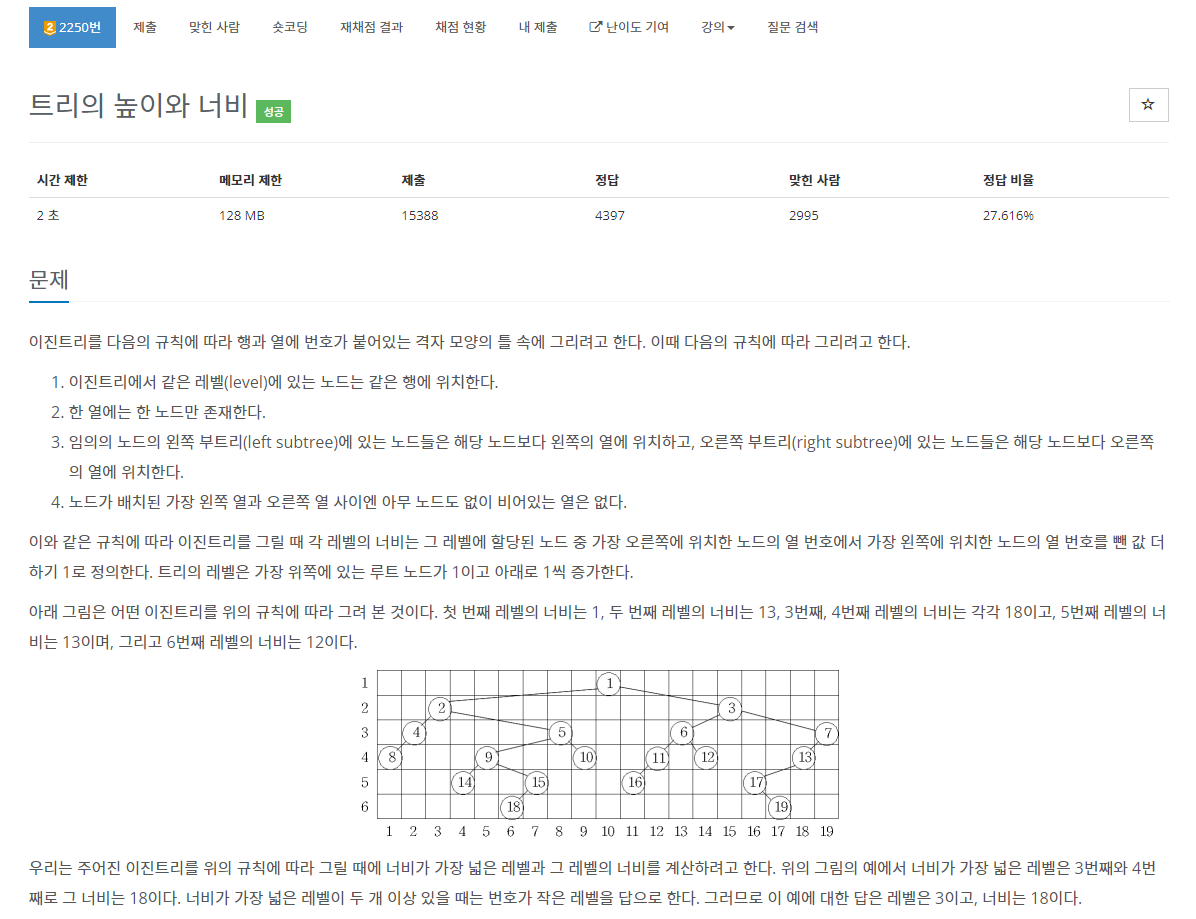
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2250
2250번: 트리의 높이와 너비
첫째 줄에 노드의 개수를 나타내는 정수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 10,000)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 각 줄마다 노드 번호와 해당 노드의 왼쪽 자식 노드와 오른쪽 자식 노드의 번호가 순서대로 주어진다.
www.acmicpc.net
[변수 설명]
- int n : 노드의 개수
- int curr_col : 현재 노드를 배치할 열 ( curr_col - 1번째 열까지는 배치 완료되어 있음 )
- int tree[MAX][2] : 트리 정보, tree[node][0]은 node의 왼쪽 자식 노드, tree[node][1]은 node의 오른쪽 자식 노드
- vector<pair<int, int>> depth_width : 각 레벨의 양 끝 노드 정보, depth_width[i].first는 i 레벨의 왼쪽 끝 노드, depth_width[i].second는 i 레벨의 오른쪽 끝 노드
- int col[MAX] : col[node] = node가 위치한 열
- int node[MAX] : 루트 노드를 찾기 위한 배열, node[i] = 노드 i가 입력받은 횟수, node[i]가 1이라면 i는 루트 노드
[풀이 과정]
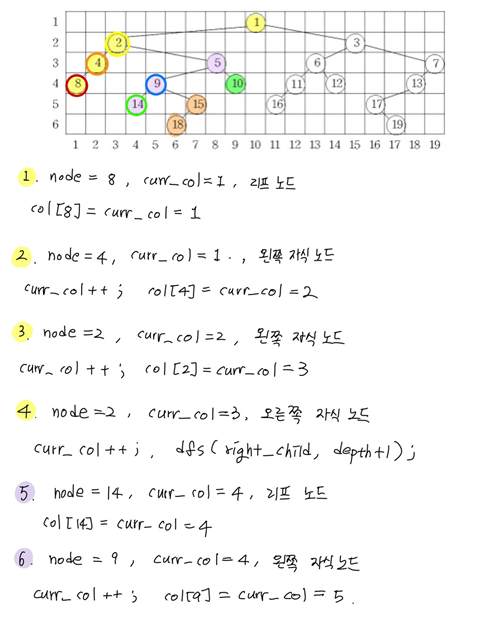
1. 먼저 트리에 대한 정보를 입력받아 tree를 완성하고 루트노드를 찾습니다.
2. dfs(root, 1) 을 호출하여 depth는 1이고 루트노드는 root인 노드부터 탐색을 시작합니다.
3. tree를 통해 인자로 받은 노드의 왼쪽자식노드, 오른쪽자식노드를 얻습니다.
4. 자식 노드의 유무에 따라 col[num]을 세팅하고 dfs()를 재귀호출합니다.
4-1. 자식 노드가 모두 없다면, 리프노드이므로 col[num]=curr_col 로 설정하여 노드 num의 위치를 curr_col 열에 배치시킵니다.
4-2. 자식 노드가 모두 있다면, 왼쪽 자식노드 방향으로 리프 노드를 만날때까지 dfs()를 실행합니다. 실행되고 나면 현재 노드인 num의 왼쪽 자식 노드쪽으로의 모든 후손 노드들이 알맞은 열 위치에 배치 됩니다. 그리고 나서 현재 노드를 배치한 뒤, 오른쪽 자식 노드 쪽으로 dfs()를 호출합니다.
4-3. 오른쪽 자식 노드만 있다면, 현재 열의 위치가 현재 노드가 배치될 위치이므로 배치를 시키고 오른쪽 노드쪽으로 dfs()를 호출합니다.
4-4. 왼쪽 자식 노드만 있다면, 4-2의 왼쪽 자식노드 방향으로의 과정과 동일하게 처리합니다.
5. col[num] 이 세팅이 완료되면, 현재 depth의 왼쪽끝 노드와 양쪽끝 노드를 세팅해야 합니다. 이때 왼쪽끝 노드인 first는 처음 한 번만 설정해야하고, second는 탐색을 할 수록 갱신해야 합니다.
6. 모든 노드를 탐색할 때까지 3~5 과정을 반복합니다.
7. 탐색이 완료되면 depth_width에 저장된 정보를 통해 가장 큰 너비와 그때의 레벨을 구합니다.
고뇌의 흔적...ㅎㅎ
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10001
int n;
int curr_col = 1;
int tree[MAX][2];
vector<pair<int, int>> depth_width;
int col[MAX];
int node[MAX];
void dfs(int num, int depth) {
int left_child = tree[num][0];
int right_child = tree[num][1];
if (left_child == -1 && right_child == -1) { //리프 노드
col[num] = curr_col;
}
else if (left_child != -1 && right_child != -1) { //둘 다
dfs(left_child, depth + 1);
curr_col++;
col[num] = curr_col;
curr_col++;
dfs(right_child, depth + 1);
}
else if (left_child == -1 && right_child != -1) { //오른쪽
col[num] = curr_col;
curr_col++;
dfs(right_child, depth + 1);
}
else if (left_child != -1 && right_child == -1) { //왼쪽
dfs(left_child, depth + 1);
curr_col++;
col[num] = curr_col;
}
if (depth_width[depth].first == 0)
depth_width[depth].first = num;
depth_width[depth].second = num;
}
int main(void) {
int ans_width = 0;
int ans_depth = 0;
cin >> n;
depth_width.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int p, lc, rc;
cin >> p >> lc >> rc;
node[p]++;
if (lc != -1)
node[lc]++;
if (rc != -1)
node[rc]++;
tree[p][0] = lc;
tree[p][1] = rc;
}
int root;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (node[i] == 1)
root = i;
}
depth_width[0] = { 0, 0 };
dfs(root, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < depth_width.size(); i++) {
int left = depth_width[i].first;
int right = depth_width[i].second;
int width = col[right] - col[left] + 1;
if (left == 0 && right == 0)
break;
if (ans_width < width) {
ans_width = width;
ans_depth = i;
}
}
cout << ans_depth << " " << ans_width;
return 0;
}
'알고리즘 문제 풀이 > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 BOJ][C++]16940번 BFS 스페셜 저지 풀이: BFS (0) | 2022.05.03 |
|---|---|
| [백준 BOJ][C++]1068번 트리 풀이: DFS (0) | 2022.04.29 |
| [백준 BOJ][C++]9663번 N-Queens 풀이: DFS & 백트래킹 (0) | 2022.04.27 |
| [백준 BOJ][C++]1967번 트리의 지름 풀이: DFS (0) | 2022.04.26 |
| [백준 BOJ][C++]1261번 알고스팟 풀이: BFS (0) | 2022.04.25 |




