| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
- HTML #CSS
- 컴퓨터공학 #c #c언어 #문자열입력
- 컴퓨터공학 #Java #자바 #클래스 #객체 #인스턴스
- BOJ #컴퓨터공학 #C++ #알고리즘 #자료구조
- 잔
- 컴퓨터공학 #자료구조 #스택 #c++ #알고리즘 #백준문제풀이
- Today
- Total
영벨롭 개발 일지
[백준 BOJ][C++]16947번 서울 지하철 2호선 풀이: BFS & DFS 본문
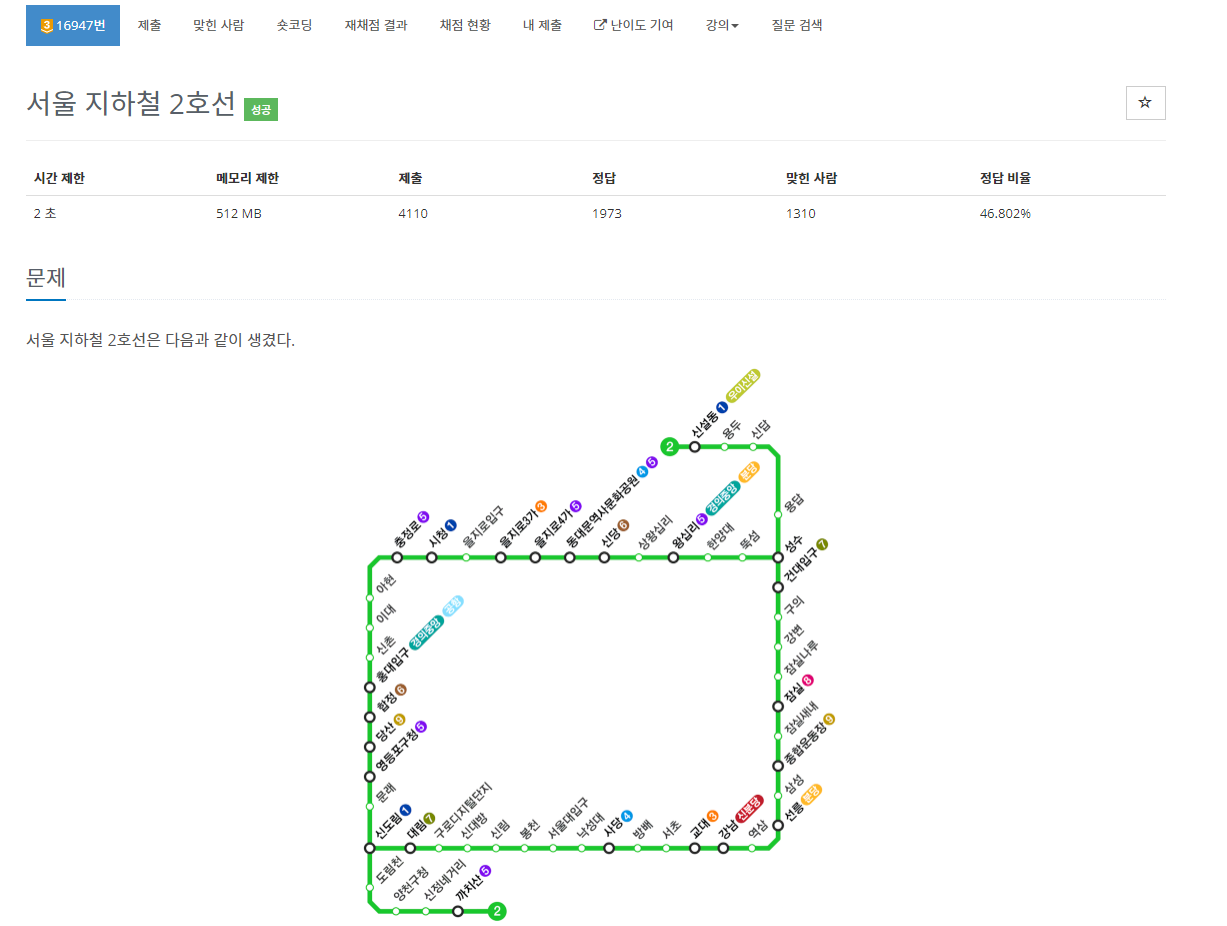
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/16947
16947번: 서울 지하철 2호선
첫째 줄에 역의 개수 N(3 ≤ N ≤ 3,000)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 역과 역을 연결하는 구간의 정보가 주어진다. 같은 구간이 여러 번 주어지는 경우는 없고, 역은 1번부터 N번까지 번호
www.acmicpc.net
[전체 풀이 과정]
1. graph에 edge 정보를 입력
2. 각 노드에 대해 bfs() 실행하여 circle 찾기
3. circle을 찾으면 dfs() 를 실행하여 각 거리 정보를 저장 후 프로그램 종료
[ BFS 풀이 과정 ]
1. 지하철 역 1번부터 n번까지 각 역의 번호를 시작 번호로 하여 bfs(int start) 호출
2. 만약 graph[start].size() 가 2보다 작다면 circle을 만들 수 없으므로 return
3. start 방문 표시 후, queue에 start에 대한 정보(num=start, depth=1, parent=NULL)를 push
4. queue의 front() 원소를 curr에 저장 후, pop()
5. graph[curr->num]에 연결된 역 번호를 탐색
6. 만약 아직 방문하지 않은 역이라면 queue에 push (child={next, curr->depth+1, curr})
7. 이미 방문한 역 중, start의 동일한 역이고 depth가 3 이상이라면 circle 찾은 것이므로 flag=true
8. 이미 방문한 역 중, start와 동일하지 않고 curr의 부모 노드의 번호가 아니라면 queue에 push
9. flag가 true일 때, curr부터 curr의 모든 부모 노드에 해당하는 번호를 circle[tmp->num]=0으로 초기화, 이때 circle 내에 중복된 번호가 있다면(if(circle[tmp->num]==0)이라면 circle이 아니므로 return
10. queue가 비었거나, bfs가 종료될때까지 4~9번 반복
[ DFS 풀이 과정 ]
1. circle을 찾았다면 circle[i] == 0인 번호에 대해 dfs(i, 0) 실행
2. graph[i]에 연결된 역 중, 아직 방문하지 않고 circle이 0이 아니라면 방문 표시후 circle=depth+1로 set 후 dfs 재귀호출
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<int> graph[3001];
int circle[3001] = { 1, };
bool visit[3001] = { false, };
bool findCircle = false;
typedef struct node {
int num;
int depth;
node* parent;
};
void bfs(int start) {
if (graph[start].size() < 2)
return;
queue<node*> q;
bool flag = false;
visit[start] = true;
node* start_node = new node;
start_node->num = start;
start_node->depth = 1;
start_node->parent = NULL;
q.push(start_node);
while (!q.empty()) {
node* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[curr->num].size(); i++) {
int next = graph[curr->num][i];
if (!visit[next]) {
visit[next] = true;
node* child = new node;
child->num = next;
child->depth = curr->depth + 1;
child->parent = curr;
q.push(child);
}
else {
if (next == start && curr->depth >= 3) {
flag = true;
}
else if (next != start && next != curr->parent->num) {
node* child = new node;
child->num = next;
child->depth = curr->depth + 1;
child->parent = curr;
q.push(child);
}
}
}
if (flag && curr->depth >= 3) {
memset(circle, 1, sizeof(circle));
node* tmp = curr;
while (tmp != NULL) {
if (circle[tmp->num] == 0)
return;
circle[tmp->num] = 0;
tmp = tmp->parent;
}
findCircle = true;
return;
}
}
}
void dfs(int num, int depth) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph[num].size(); i++) {
int child = graph[num][i];
if (circle[child] != 0 && !visit[child]) {
visit[child] = true;
circle[child] = depth + 1;
dfs(child, depth + 1);
}
}
}
void find_circle() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
memset(visit, false, sizeof(visit));
bfs(i);
if (findCircle) {
memset(visit, false, sizeof(visit));
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (circle[j] == 0) {
dfs(j, 0);
}
}
return;
}
}
}
int main(void) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
find_circle();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << circle[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
'알고리즘 문제 풀이 > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 BOJ][C++]1261번 알고스팟 풀이: BFS (0) | 2022.04.25 |
|---|---|
| [백준 BOJ][C++]14226번 이모티콘 풀이: BFS (0) | 2022.04.25 |
| [백준 BOJ][C++]2206번 벽 부수고 이동하기 풀이: BFS (0) | 2022.04.12 |
| [백준 BOJ][C++]7562번 나이트의 이동 풀이: BFS (0) | 2022.04.11 |
| [백준 BOJ][C++]7569번 토마토 풀이: BFS (0) | 2022.04.11 |




